| [1] Jang YY,Collector MI,Baylin SB,et al.Hematopoietic stem cells Convert into liver cells within days without fusion.Nat Cell Biol.2004;6(6):532-539. [2] 安伟德,胡祥,曹亮,等.骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化肝细胞及肝内移植研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(8):917- 919. [3] Kakinuma S,Tanaka Y,Chinzei R,et al.Human umbilical cord blood as a source of transplantable hepatic progenitor cells.Stem Cells.2003;21:217-227. [4] Wang XL,Ge SL,George M,et al.Albumin2expressing hepatocyte like cells develop in the liver of immunodeficient mice that received tranplants of highly purified human hematopoietic stem cell.Blood.2003; 101(10):4201-4208. [5] Sei K,Yujiko T,Rroko C,et al.Human umbilical cord blood as a source of tranplantable hepatic progenitor cells.Stem Cells.2003;21(2):217-227. [6] Eric L,Heather C.Purified hematopoietic stem cells can difFerntiate into hepatocytes in vivo.Nat Med.2000;6: 1229-1234. [7] Zhang FT,Wan HJ,Li MH,et al.Transplantation of microencapsulated umbilical-cord-blood-derived hepatic-like cells for treatment of hepatic failure .World J Gastroenterol.2011;17(7):983-945. [8] Nga BY,Forte V,Campisi P.Molecular Angiogenic Signalingin Angiofibromas After Embolization.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2008;134(11):1170-1176. [9] Taylor CJ,Bolton EM,Pocock S,et al.Banking on human embryonic stem cells:estimating the number of donor cell lines needed for HLA matching. Lancet.2005; 366 (9502):2019-2025. [10] Hall AA,Guyer AG,Leonardo CC,et al.Human umbilical cord blood cells directly suppress ischemic oligodendrocyte cell death.J Neurosci Res.2009;87(2) 333-341. [11] Fernandez MN.Improving the outcome of cord blood transplant-ation use of mobilized HSC and other cells from third party donors.Br J Haematol.2009; 147: 1661-176. [12] Mayani H,Lansdoorp PM.Biology of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Hematopoietic Stem-Progenitor Cells.Stem Cells.1998;16:153-165. [13] Tintut Y,Alfonso Z,Saini T,et aL Multilineage Potential of CellsFrom the Artery Wall.Circulation.2003; 108: 2505-2510. [14] Reddi AS,Kuppasani K,Ende N,et al.Human umbilical cord blood as an emerging stem cell therapy for diabetes mellitus.Stem Cells.2010;5:356-361. [15] 江学良,权启镇,孙自勤.干细胞治疗失代偿期肝硬化应注意的问题[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2010,8(2):48-51. [16] Smythe J,Armitage S,McDonald D,etal.Directed Sibling Cord Blood Banking for Transplantation:The 10-Year Experience in the National Blood Service in England.Stem Cells.2007;25(8):2087-2093. [17] 徐朝霞,曾荣灵.38例骄带血治疗慢性肝炎免疫学观察[J].中国医师杂志,2003,5(8):1106-1107. [18] 唐晓鹏,王文龙,张旻,等.脐血有核细胞输注治疗慢性肝衰竭的初步临床观察[J].中国输血杂志,2008,21(6):420- 423. [19] 杜玲,罗国君,袁雅红.肪血干细胞静脉输注治疗失代偿期肝硬化1例并文献复习[J].现代生物医学进展,2009,9(18): 3511-3513. [20] Tang XP,Zhang M,Yang X,et al.Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood stem cells into hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro.World J Gastroentrol. 2006;12(25):4014-4019. [21] Lepus CM,Gibson TF,Gerber SA,et al.Comparison of human fet al liver,umbilical cord bloodand adult blood hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in NOD-scid/γc-/-, Balb/c-Rag1-/-Yc-/-,and C.B-17-scid/bg immunodeficient mice. Hum Immunol.2009; 70(10):790-802. [22] Elkhafif N,El Baz H,Hammam O,et al.CD133+ human Umbilical cord blood stem cells enhance angiogenesis in experimental chronic hepatic fibrosis.APMIS. 2011; 9(1):66-75. [23] Li S,Sun Z,Lv G,et al.Microencapsulated UCB cells repair hepatic injure by intraperitoneal transplantation. Cytotherapy.2009;11(8):1032-1040. [24] 谭国胜,向贤宏,王于,等.脂肪间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肝硬化模型的治疗作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2009, 17(11): 1074-1078. [25] 李行.肝硬化疾病凝血四项与D-二聚体联检的应用[J].中外健康文摘,2013,29(15):154. [26] Takami T,Terai S,Sakaida I.Advanced therapies using autologous bone marrow cells for chronic liver disease. Discov Med.2012;14(74):7-12. [27] Hwang S,Hong HN,Kim HS,et al.Hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis.Cell Biol Int.2012,36(3):279-288. [28] Takami T,Terai S,Sakaida I.Stem cell therapy in chronic liver disease.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28(3): 203-208. [29] Russo FP, Parola M. Stem cells in liver failure.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.2012;26(1):35-45. [30] 高远征,贾素华,刘玉英,等.异基因脐血干细胞移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化的疗效观察[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2010, 26(6):613-617. |
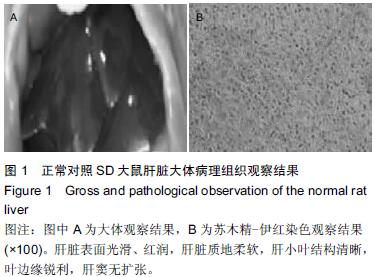
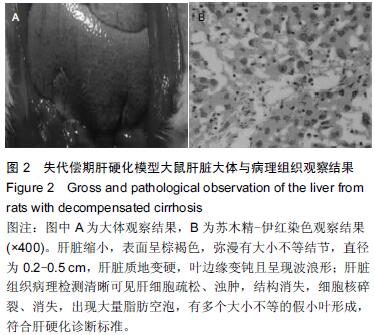
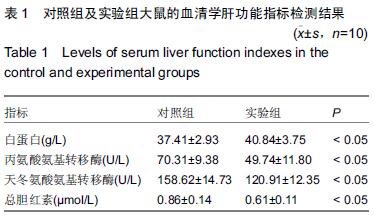
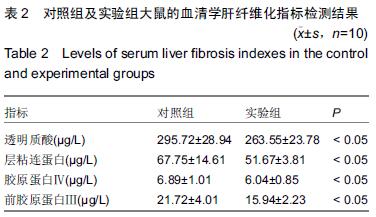
.jpg)
.jpg)